Understanding Manifold Valves: Essential Components in Fluid Control Systems
March 2, 2024
Instrument Valves: A Detailed Overview
October 7, 2024A manifold valve is a crucial component in various systems, from hydraulic and pneumatic systems to automotive engines. Its role is to control the flow of fluid or gas, directing it to different outlets or combining flows from multiple sources. Understanding how a manifold valve working is essential for anyone involved in engineering, maintenance, or operation of such systems.
What is a Manifold Valve?
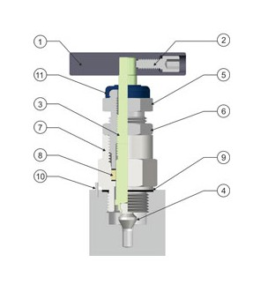
A manifold valve is essentially a distribution hub for fluids or gasses. It consists of a main body with multiple inlet and outlet ports. These ports are connected internally by channels or passages, allowing for the controlled flow of the medium. The valve’s operation is controlled by various mechanisms, including manual, hydraulic, pneumatic, or electrical actuators.
Types of Manifold Valves
Manifold valves come in various types, each designed for specific applications. Some common types include:
- Distribution manifold valves: These valves distribute fluid or gas from a single source to multiple outlets. They are commonly used in hydraulic systems for controlling actuators.
- Collector manifold valves: These valves combine fluid or gas from multiple sources into a single outlet. They are often used in pneumatic systems to increase airflow.
- Selector manifold valves: These valves allow the selection of fluid or gas from different sources and direct it to a single outlet. They are commonly used in hydraulic systems for switching between different pump outputs.
How a Manifold Valve Works
The basic principle behind a manifold valve’s operation is relatively simple. Fluid or gas enters the manifold through an inlet port. Inside the valve body, the fluid is directed through internal passages to the desired outlet ports based on the valve’s position or control signal.
The specific mechanism for controlling the flow varies depending on the valve type. Some common methods include:
- Spool valves: A spool moves within the valve body to open and close different ports.
- Poppet valves: A poppet lifts or seats to control the flow of fluid or gas.
- Ball valves: A ball rotates within the valve body to open or close ports.
Applications of Manifold Valves
Manifold valves find applications in a wide range of industries and systems. Some common examples include:
- Hydraulic systems: Used for controlling actuators, such as cylinders and motors, in construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and industrial automation.
- Pneumatic systems: Used for controlling actuators, such as cylinders and valves, in factory automation, packaging machines, and robotics.
- Automotive engines: Used for distributing fuel and coolant to different engine components.
- Chemical processing plants: Used for controlling the flow of various chemicals and fluids.
Benefits of Using Manifold Valves
Manifold valves offer several advantages:
- Efficiency: They allow for precise control of fluid or gas flow, reducing waste and energy consumption.
- Flexibility: They can be configured to meet various system requirements and can be easily modified or expanded.
- Compactness: They often have a smaller footprint compared to multiple individual valves, saving space.
- Reliability: Well-designed manifold valves are known for their durability and long service life.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
To ensure optimal performance and longevity, regular maintenance of manifold valves is essential. This includes checking for leaks, cleaning internal passages, and lubricating moving parts.
Common issues with manifold valves include:
- Leaks: Caused by worn seals, damaged gaskets, or loose connections.
- Restricted flow: Caused by debris or deposits in the internal passages.
- Malfunction: Caused by electrical or hydraulic failures in the control system.
By understanding the causes of manifold valve problems, you can effectively troubleshoot and repair manifold valves.
Conclusion
Manifold valves are indispensable components in numerous systems. Their ability to control fluid or gas flow efficiently and precisely makes them invaluable in various industries. By understanding their working principles, types, and applications, you can optimize their use and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.