Some important Applications of Ball Valve in High-Pressure Environments
August 29, 2022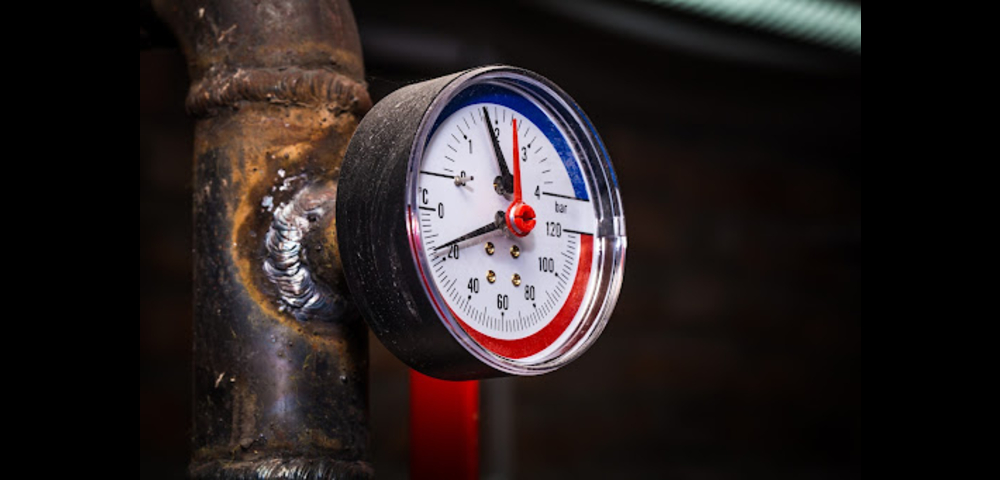
How to Use a Pressure Gauge with Ball Valve?
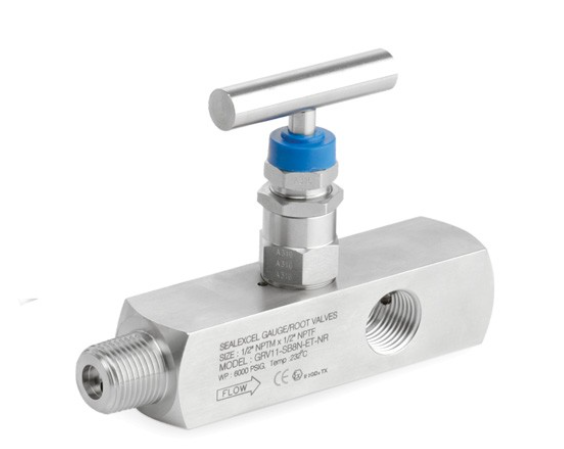
February 5, 2023Manifolds are parts of a hydraulic system that connect two or more valves. Several block/isolate valves can be put on the same body. Each of these valves has a hole below it where a pipe can be connected. All of them have the same main body or valve chamber. Ball, bleed, needle, and vent valves are often found on these manifolds. When you use them, you save on space and installation costs.
What Is The Purpose Of A Ball Valve Manifold?
A ball valve manifold is meant to stop or slow the flowing fluid in a system so that the process media can be kept separate from the pressure instrumentation. A block-and-bleed manifold separates or blocks the process media upstream from the instrumentation. The remaining fluid in the system can be bled off or vented on the downstream side of the manifold.
A block-and-bleed manifold separates or blocks the process media upstream from the instrumentation. The remaining fluid in the system can be bled off or vented on the downstream side of the manifold.
The advantages of a manifold valve
Ball valve manifolds are used in many things, from small, portable machines to large, heavy industrial ones. Choosing the right valve manifold for an application can be hard and complicated, especially when there are many options and things to think about. Here are reasons why a valve manifold might be the right choice for your application.
High Efficiency:
Due to the size of the opening in the ball, ball valves are called “high recovery” valves because they have a low-pressure drop and a high flow capacity. When the valve is fully open, there is not much resistance to fluid flow.
Convenient Usage:
The ball valve manifold works well and is easy to use because you only have to turn them a quarter turn. The valve is not too heavy or too big so it can be put in place and taken out without too much trouble.
Low maintenance:
Because ball valves are simple, they do not need as much maintenance as other valves. As the stem of a ball valve manifold only turns and does not move in any other direction, the packing seal on the stem is not easily worn or broken. When it comes to fixing ball valves, they are easy to take apart, and it is simple to replace worn parts.
Ease of Installation:
A step in the configuration process often missed is mounting the valve manifold. Valve manifolds can be attached directly to a machine or a DIN rail. Many of them can be mounted either vertically or horizontally, giving you even more options.
Easy Field Maintenance and Valve Replacement:
Plug-in sub-base manifolds make it easy and quick to replace valves, which can help cut down on process downtime. Valve slices are taken off by unscrewing the two screws on each slice, which is also how new valves are put in. The manifold’s silencers and push-in fittings are also easy to replace. On the other hand, if your application needs to change or your specified ball valve manifold needs to be changed, expansion kits may be available that can be used to expand a valve manifold in the field easily.
Cost-efficient:
The price of a ball valve manifold is not too high compared to other types of valves. Also, they are cheaper to keep up with over time because they don’t need much care.
Robust:
Ball valve manifolds are the most durable because they can handle high pressures. They come in many different materials used in different places and industries.
Reliable Technical Support:
It is important to have customer support teams that have worked on industrial application solutions for decades and can help customers with their ball valve manifold needs. If you want to use a valve manifold inside a control cabinet, are working on an electro-pneumatic control system, or need help choosing the right manifold for your application, there are technical and customer support teams available to help.
A metal sealed ball valve manifold can be used in the piping system or device of the high-temperature medium in metallurgy systems, electric power systems, petrochemical equipment, and city heating systems. If you need to control the flow, choose a worm-drive, pneumatic, or electric regulating ball valve with a v-shaped opening.
Water treatment systems can use a common thread ball valve or a flange ball valve. They can also be fitted with pneumatic or electric actuators and industrial automation to improve engineering efficiency.



