Benefits of using Instrument valves and fittings
November 29, 2021
Choosing And Sizing Process Flow Control Valves: A Guide
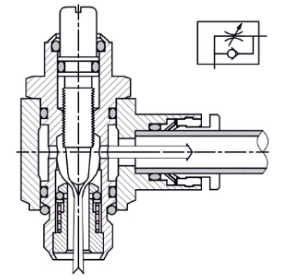
July 5, 2022Check valves are used in almost every sector that uses pipework to transfer fluids. A check valve permits just one direction of flow while prohibiting reverse flow, or flow in the opposite direction. The hydraulic pressure from the flow of water acting on the valve mechanism causes these valves to open and shut.
Flow regulator valves are often used in steam lines, condensate lines, water lines, HVAC systems, and chemical feed pumps, to mention a few. Because reverse flow may be exceedingly harmful to certain equipment, these valves are crucial components in many scenarios. As a result, check valve failure symptoms must be discovered as soon as possible to avoid facility downtime and expensive repairs.
Proper and consistent preventive maintenance is the key to avoiding pneumatic check valve failure and guaranteeing valve life.
How to Extend the Life of a Check Valve
Check valves are an essential component of fluid-transporting pipes. A correctly working check valve enables liquid to flow in one direction while preventing reverse flow. To maintain the pneumatic check valve in good working order, proper installation and preventive valve maintenance are required.
It is critical to consider flow capacity during installation. Proper valve size is required to avoid performance difficulties. Oversizing may cause vibration damage, reducing the check valve’s life duration. Routine maintenance on a properly sized check valve, on the other hand, may avoid leakage and early failure.
Implementing Preventative Measures
The first stage in valve maintenance is to ensure that the pipeline and valves are clean and debris-free. Filters are an easy and efficient technique to keep junk out of the system. If the material does get into the pipework, cleanse the pipes to eliminate settled particles and limit accumulation. Establishing a consistent maintenance plan for all check valves is critical.
Selecting the Correct Check Valve
This procedure may increase the system’s functionality and durability. Choose a correctly sized flow regulator valve based on vertical or horizontal orientation, media type, and the generally anticipated flow condition particular to the application—not on pipeline size. Incorrectly, sized valves may increase costs, lower flow velocity, and create problems like water hammers. The valves must be placed properly and utilized by the manufacturer’s instructions for best performance.
Maintenance to Keep Tight Shut Off
A system may need adequate routine inspections from time to time to maintain tight shutdown and avoid premature check valve failure. By eliminating any foreign stuff, you can maintain a tight seal. If flushing has not worked, remove and dismantle the valve altogether. Examine the valve seat and the disc for scratches. Then, wash all of the components in the system’s clean fluid. Inspect the housing and trim pieces for corrosion or erosion while you reassemble the valve.
If there is rust or severe roughness due to erosion, replace the valve. Though all check valves are conceptually identical, they differ substantially in terms of internal valve mechanics, opening pressures, and construction materials. Internal devices in these valves are also sensitive to debris, flow velocities, and pressure spikes. As a result, correct pneumatic check valves and frequent inspection are critical for avoiding premature check valve failure in any kind of application.