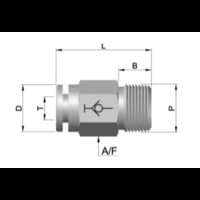
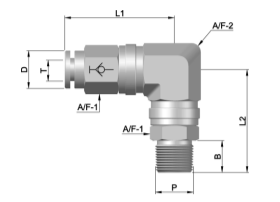
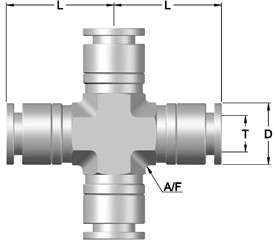
SS Tube Fittings: Secure Your Lines with Top Options
April 22, 2024
PIF Checker: Make Product Validation Easy
October 18, 2024Introduction
In the intricate world of pneumatic systems, where compressed air is the lifeblood of countless industrial processes, the role of a pneumatic flow control valve is paramount. These unassuming components are the gatekeepers of airflow, ensuring precision, efficiency, and control in every operation. In this in-depth study, we get into the complex nature of pneumatic flow control valves, discovering their types, functions, and applications, as well as the crucial role they play in maximizing system performance.
Understanding Pneumatic Flow Control Valves
A pneumatic flow control valve is essentially a device designed to regulate the rate of airflow in a pneumatic system. By strategically controlling the volume of air passing through, these valves enable precise adjustments to system parameters such as speed, force, and pressure. This level of control is indispensable in a myriad of industrial applications, from manufacturing and packaging to automotive and aerospace.
How does a pneumatic flow control valve work?
The functionality of a pneumatic flow control valve is relatively straightforward. It comprises a valve body, an actuator, and a control mechanism. As compressed air enters the valve, the control mechanism, often a needle or a throttle, restricts the airflow, thereby regulating the output. This controlled airflow can then be directed to various components within the pneumatic system, such as cylinders, actuators, or other valves.
Types of Pneumatic Flow Control Valves
Pneumatic flow control valves come in various designs, each catering to specific application requirements.
- Needle Valves: These valves offer precise control over airflow through a fine needle adjustment. They are ideal for applications demanding minute adjustments to flow rates.
- Throttle Valves: Equipped with a tapered orifice, throttle valves provide a broader range of flow control. They are frequently employed in applications that call for regular modifications.
- Check Valves: While primarily used to prevent reverse flow, check valves can also indirectly influence airflow by restricting it in one direction.
- Proportional Valves: These advanced valves allow for continuous and proportional control of airflow based on an electrical input signal. They are often employed in complex automation systems.
Applications of Pneumatic Flow Control Valves
The versatility of pneumatic flow control valves makes them indispensable across a wide range of industries.
- Manufacturing: In assembly lines, these valves regulate the speed of pneumatic tools, ensuring consistent and efficient operations.
- Packaging: From filling machines to sealing equipment, pneumatic flow control valves maintain precise control over packaging processes.
- Automotive: In automotive manufacturing, these valves are crucial for controlling actuators in assembly, testing, and painting processes.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry relies on pneumatic flow control valves for critical functions in aircraft systems, such as landing gear and flight controls.
- Medical Equipment: Pneumatic systems in medical equipment often incorporate flow control valves to regulate the flow of gases and fluids.
Benefits of Using Pneumatic Flow Control Valves
The integration of pneumatic flow control valves in a system offers numerous advantages, including:
- Precision Control: Enables fine-tuning of airflow for optimal system performance.
- Efficiency: reduces energy consumption by preventing excessive airflow.
- Reliability: Long-term functionality and low maintenance are guaranteed by durable construction.
- Versatility: appropriate for many different industries and applications.
- Cost-Effective: Provides a cost-efficient solution for airflow control.
Selecting the Right Pneumatic Flow Control Valve
Choosing the appropriate pneumatic flow control valve is crucial for achieving the desired system performance. Key factors to consider include:
- Flow Rate Requirements: Determine the required airflow for the application.
- Pressure Rating: Ensure the valve can withstand the operating pressure.
- Material Compatibility: Select a valve compatible with the fluid medium.
- Mounting Options: Choose a valve with suitable mounting configurations.
- Control Mechanism: Select the appropriate control mechanism based on application needs.
Maintenance and troubleshooting
Proper maintenance of pneumatic flow control valves is essential for their longevity and optimal performance. Regular inspection, cleaning, and lubrication are recommended. Common issues, such as leaks, reduced flow, or erratic operation, can often be resolved through basic troubleshooting steps.
Conclusion
Pneumatic flow control valves are unsung heroes in the realm of automation and industrial processes. Their ability to precisely regulate airflow is instrumental in achieving efficient, reliable, and controlled operations. By understanding their functions, types, and applications, engineers and technicians can effectively harness the power of these valves to optimize system performance and drive productivity. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated pneumatic flow control solutions to emerge, further expanding the possibilities for innovation and efficiency in various industries.